题目
There are a total of n courses you have to take, labeled from 0 to n-1.
Some courses may have prerequisites, for example to take course 0 you have to first take course 1, which is expressed as a pair: [0,1]
Given the total number of courses and a list of prerequisite pairs, is it possible for you to finish all courses?
Example 1:1
2
3
4Input: 2, [[1,0]]
Output: true
Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take.
To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So it is possible.
Example 2:1
2
3
4Input: 2, [[1,0],[0,1]]
Output: false
Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take.
To take course 1 you should have finished course 0, and to take course 0 you should also have finished course 1. So it is impossible.
Note:
- The input prerequisites is a graph represented by a list of edges, not adjacency matrices. Read more about how a graph is represented.
- You may assume that there are no duplicate edges in the input prerequisites.
题目分析
- 题意比较容易理解,就是需要选修某一门课程的时候,需要先修某一门课程,给出一组课程的先修关系,问是否能完成课程。这个问题可以抽象为有向图求是否有环路问题,课程的先修关系是一个有向边,每一门课程就是一个点。
- 问题抽象成有向图求是否存在环路问题,思考有向图求存在环路的方法。
拓扑排序实现
- 什么是拓扑排序?
对一个有向无环图(Directed Acyclic Graph简称DAG)G进行拓扑排序,是将G中所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得图中任意一对顶点u和v,若边(u,v)∈E(G),则u在线性序列中出现在v之前。通常,这样的线性序列称为满足拓扑次序(Topological Order)的序列,简称拓扑序列。简单的说,由某个集合上的一个偏序得到该集合上的一个全序,这个操作称之为拓扑排序。
- 为什么用拓扑排序?
如果能够用拓扑排序完成对图中所有节点的排序的话,就说明这个图中没有环,而如果不能完成,则说明有环
怎样进行拓扑排序?
- 建立图的邻接表
- 然后找出入度数为0的点
- 删除入度数为0的点,将其指这些点的边也删除,同时将这些点加入到结果队列中
- 重复2,直到没有点的入度为0
- 判断是否仍存在未被加入的点,若存在证明有环
当然本题不需要这么完整的步骤,不需要得到排序结果什么的,只需要最后判断下是否有环,然后返回
true或者false- 时间复杂度:$O(V+E)$
DFS实现
- 需要对DFS有一定深入的了解,了解树边,前向边等等
需要DFS稍加变化,来解决这个问题。解决的方法如下:
图中的一个节点,根据其
vertexState[i]的值,有三种状态:点的状态
- -1 - 已被访问过,正在访问其后代节点
- 0 - 未被访问过
- 1 - 已被访问过,且其子节点亦全部访问过
按照这样的假设,当按照DFS进行搜索时,碰到一个节点时有三种可能:
1、如果vertexState[V]=0,这是一个新的节点,未被访问过,进行dfs搜索
2、如果vertexState[V]=-1,说明是在访问该节点的后代的过程中访问到该节点本身,则图中有环。
3、如果vertexState[V]=1,该点已经被访问过,且以该点与其后代节点构成的一个子图是一个非强连通图,则遇到这类点不可能有环存在。时间复杂度:$O(V)$
实现代码
解法1 - 拓扑排序
- 拓扑排序思路
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41// 解法 1
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<pair<int, int>>& prerequisites) {
if(numCourses <= 1) return true;
int n = numCourses;
vector<set<int> > myVec(numCourses);
for(auto it : prerequisites)
myVec[it.first].insert(it.second);
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) {
if(myVec[i].size() == 0)
q.push(i);
}
while(!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
n -= size;
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
int tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < numCourses; ++j) {
if(j == tmp) continue;
if(myVec[j].find(tmp) != myVec[j].end()) {
myVec[j].erase(myVec[j].find(tmp));
if (myVec[j].size() == 0)
q.push(j);
}
}
}
}
if(n > 0)
return false;
else
return true;
}
};
拓扑排序优化 — Course Schedule ll中思路
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40// 解法 1 优化
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<pair<int, int>>& prerequisites) {
int inDegree[numCourses] = {0}; // 记录课程需要先修课程的数量
// 对应存储需要修完该课程才能修的课程
vector<set<int> > myVec(numCourses);
for(auto it : prerequisites) {
inDegree[it.first]++;
myVec[it.second].insert(it.first);
}
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) {
if(inDegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
while(!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
numCourses -= size;
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
int tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
// 此处的引用很精髓!!!!
for (auto &j : myVec[tmp]) {
inDegree[j]--;
if(inDegree[j] == 0) {
q.push(j);
}
}
}
}
return numCourses == 0;
}
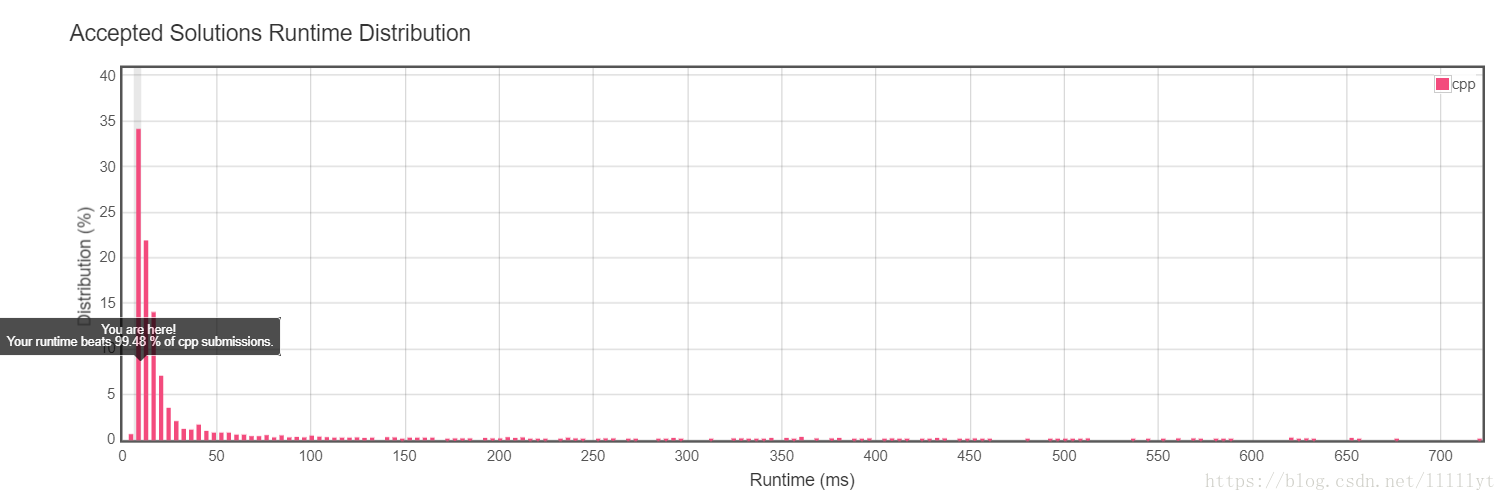
};遍历节点度数时候使用引用传递
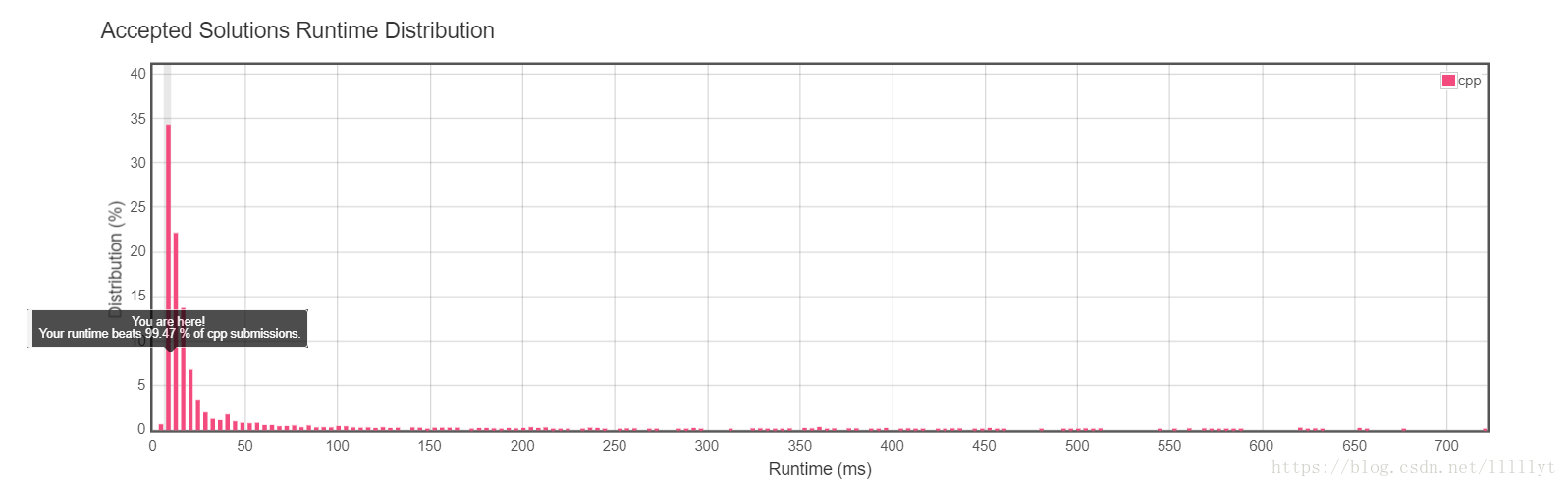
遍历节点度数时候使用值传递
引用传递:在引用传递过程中,被调函数的形式参数虽然也作为局部变量在栈中开辟了内存空间,但是这时存放的是由主调函数放进来的实参变量的地址。值传递:形参是实参的拷贝,改变形参的值并不会影响外部实参的值,形参有自己独立的存储空间,每次都需要在栈中申请内存空间并且拷贝实参。因此,引用传递比值传递需要的操作时间小多了。
解法2 - DFS
- 优化的DFS实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35// 解法 2
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<pair<int, int>>& prerequisites) {
vector<set<int> > myVec(numCourses);
for(auto it : prerequisites)
myVec[it.second].insert(it.first);
/*
* 点的状态
* -1 - 已被访问过,正在访问其后代节点
* 0 - 未被访问过
* 1 - 已被访问过,且其子节点亦全部访问过
*/
int vertexState[numCourses] = {0};
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i)
if(!dfs(i, myVec, vertexState))
return false;
return true;
}
bool dfs(int node, vector<set<int> >& myVec, int *vertexState) {
if(vertexState[node] == 1) return true;
vertexState[node] = -1;
for(int i : myVec[node]) {
if(vertexState[i] == -1) return false;
if(!dfs(i, myVec, vertexState)) return false;
}
vertexState[node] = 1;
return true;
}
};